About RFID
About RFIDRF Basics
Radio Frequency (RF) communications is based on
laws of physics that describe the behavior of electromagnetic
energy waves. For the purpose of providing a very cursory
understanding of the technology this tutorial will use very
informal terminology to describe what is happening.
General physics of radio signals
RF communication works by creating
electromagnetic waves at a source and being able to pick up
those electromagnetic waves at a particular destination. These
electromagnetic waves travel through the air at near the speed
of light. The wavelength of an electromagnetic signal is
inversely proportional to the frequency; the higher the
frequency, the shorter the wavelength.
Frequency is measured in Hertz (cycles per
second) and radio frequencies are measured in kilohertz (KHz or
thousands of cycles per second), megahertz (MHz or millions of
cycles per second) and gigahertz (GHz or billions of cycles per
second). Higher frequencies result in shorter wavelengths. The
wavelength for a 900 MHz device is longer than that of a 2.4 GHz
device.
In general, signals with longer wavelengths
travel a greater distance and penetrate through, and around
objects better than signals with shorter wavelengths.
How does an RF communication system work?
Imagine an RF transmitter wiggling an electron
in one location. This wiggling electron causes a ripple effect,
somewhat akin to dropping a pebble in a pond. The effect is an
electromagnetic (EM) wave that travels out from the initial
location resulting in electrons wiggling in remote locations. An
RF receiver can detect this remote electron wiggling.
The RF communication system then utilizes this
phenomenon by wiggling electrons in a specific pattern to
represent information. The receiver can make this same
information available at a remote location; communicating with
no wires.
In most wireless systems, a designer has two
overriding constraints: it must operate over a certain distance
(range) and transfer a certain amount of information within a
time frame (data rate). Then the economics of the system must
work out (price) along with acquiring government agency
approvals (regulations and licensing).
How is range determined?
In order to accurately compute range ? it is
essential to understand a few terms: -
dB - Decibels
Decibels are logarithmic
units that are often used to represent RF power. To convert
from watts to dB: Power in dB = 10* (log x) where x is the
power in watts.
Another unit of measure that is
encountered often is dBm (dB milliwatts). The conversion
formula for it is Power in dBm = 10* (log x) where x is the
power in milliwatts. -
Line-of-site (LOS)
Line-of-site when
speaking of RF means more than just being able to see the
receiving antenna from the transmitting antenna. In, order
to have true line-of-site no objects (including trees,
houses or the ground) can be in the Fresnel zone. The
Fresnel zone is the area around the visual line-of-sight
that radio waves spread out into after they leave the
antenna. This area must be clear or else signal strength
will weaken.
There are essentially two parameters to look at
when trying to determine range. -
Transmit Power
Transmit power refers to
the amount of RF power that comes out of the antenna port of
the radio. Transmit power is usually measured in Watts,
milliwatts or dBm. (For conversion between watts and dB see
below.) -
Receiver sensitivity
Receiver
sensitivity refers to the minimum level signal the radio can
demodulate. It is convenient to use an example with sound
waves; Transmit power is how loud someone is yelling and
receive sensitivity would be how soft a voice someone can
hear. Transmit power and receive sensitivity together
constitute what is know as ?link budget?. The link budget is
the total amount of signal attenuation you can have between
the transmitter and receiver and still have communication
occur.
Example:
TX Power: 20dBm
RX
Sensitivity: -110dBm
Total Link budget: 130dBm.
For line-of-site situations, a mathematical formula can be
used to figure out the approximate range for a given link
budget. For non line-of-site applications range calculations
are more complex because of the various ways the signal can
be attenuated.
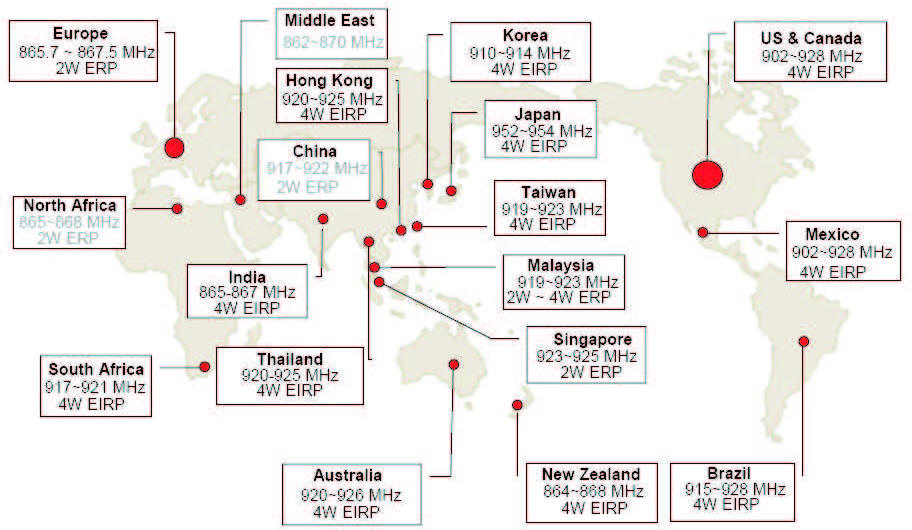
Regulations and licensing
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and
other regulatory bodies around the world have set up a series of
regulations defining the emission levels and usage for all the
different frequencies. Wireless Integrated radios operate within
the Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) bands that offer
license free operation within certain frequencies. Within the
United States, the most popular ISM band are at 902-928 MHz and
2.4 ? 2.4835 GHz. Portions of the 902-928 MHz band are also
available in Canada, Mexico, Australia and Israel. The 2.4 GHz
band is generally more accepted worldwide.
At certain power levels some regulatory agencies
require some form of spread spectrum. Spread spectrum can either
be done by frequency hopping or by direct sequence. Frequency
hopping consists of rapidly moving from one channel to the next
while maintaining synchronization with the receiver. Direct
Sequence is more complex, but works by slicing the carrier up
with a code that can be decoded at the other end. Wireless
Integrated radios uses frequency hopping as its method of spread
spectrum.
RF communications and data rate
Data rates are usually dictated by the system -
how much data must be transferred and how often does the
transfer need to take place. Lower data rates, allow the radio
module to have better receive sensitivity and thus more range.
In the RF modules the 9600 baud module has 3dB more sensitivity
than the 19200 baud module. This means about 30% more distance
in line-of-sight conditions. Higher data rates allow the
communication to take place in less time, potentially using less
power to transmit.
RFID Types
RFID is essentially available in 3 different
types, each with their own benefits and
limitations. In the Auto-ID industry UHF is the
most common but it is useful to know how to
distinguish each one.
LF (Low Frequency)
Low Frequency RFID operates at the 135kHz range
and has a very short read range (an inch or 2
normally). This type of RFID essentially
requires contact to a reader to capture the
data. While this type is not useful for product
tracking, you will find it embedded in IDs and
other key Fob applications for access/parking
control, authentication, event attendance
management, ticketing, and card payment.
HF (High Frequency)
High Frequency RFID operates at the 13.56MHz
range and has a short read range of about 5
inches normally but with specialized readers and
larger tags you can reach almost 3ft. HF RFID
tags have less interference issues than UHF so
while their range is limited they are a good
solution for small object tagging on automated
lines. High speed reading is also possible which
has made HF a good option in healthcare
environments where small vials and samples need
to be read.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency)
Ultra High Frequency RFID operates between
902-928 MHz in North America and has read ranges
up to approximately 10ft. UHF has become the
most used option in Auto-ID applications due to
its long read range and dropping costs. UHF does
have more issues with interference but a well
designed system can overcome these issues. UHF
RFID is also well suited to mounting on label
stock making it the perfect item/container level
tag option.
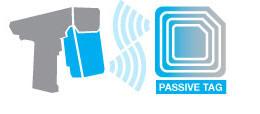
PASSIVE RFID ?
A passive tag does not contain a battery; the power is supplied by the
reader. When radio waves from the reader are encountered by a passive
tag, the coiled antenna within the tag forms a magnetic field. The tag
draws power from it, energizing the circuits in the tag. The tag then
sends the information encoded in the tag's memory.

ACTIVE RFID ?
An active RFID tag is equipped with a battery that can be used as a
partial or complete source of power for the tag's circuitry and antenna.
Some active tags contain replaceable batteries for years of use; others
are sealed units.

CONDITION SENSORS ?
Condition sensing tags not only have a battery, but also include
circuitry that reads and transmits diagnostics back to its sensor
system. The tags monitor the environmental conditions, communicate with
other items and collaborate to collect data that no single sensor would
be able to detect. The information is then fed into back-end systems
using the network software.
RFID has many applications:
RFID has many applications/uses, for example:
-
Asset management and retail sales
-
Payment by mobile phones
-
Promotion tracking (tracking of goods)
-
Access management
-
Transportation payments (toll roads)
-
Public transit (bus, rail, subway)
-
Machine readable travel documents
-
Airport Baggage Tracking Logistics
-
Museums
-
Tracking Sports memorabilia to verify
authenticity
-
Animal identification and tracking
-
Human implants, etc.
What is it and how does it work?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is the use of an object (typically
referred to as an RFID tag) applied to or incorporated into a product,
animal, or person for the purpose of identification and tracking using
radio waves. Some tags can be read from several meters away and beyond
the line of sight of the reader.
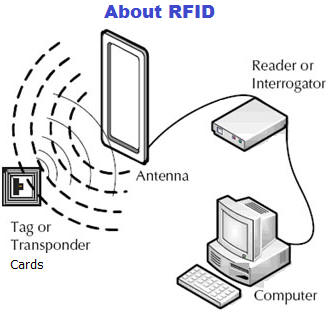
RFID comprises interrogators (also known as readers), and tags (also
known as labels).
Most RFID tags contain at least two parts. One is an integrated circuit
for storing and processing information, modulating and demodulating a
radio-frequency (RF) signal, and other specialized functions. The second
is an antenna for receiving and transmitting the signal.
There are generally three types of RFID tags: active RFID tags, which
contain a battery and can transmit signals autonomously, passive RFID
tags, which have no battery and require an external source to provoke
signal transmission, and battery assisted passive (BAP) which require an
external source to wake up but have significant higher forward link
capability providing great read range.
A library RFID tag has information (data) encoded on the tag that
contains a microchip and an antenna. The information is accessed by the
reader. The physical tag is a couple of inches square and very thin. It
has no batteries or power source as the energy needed to power and read
the tag comes from the reader, which emits a signal that searches for a
tag within its limited (?18 inches) range. When the signal hits the tag,
the tag awakens and responds.
RFID, Radio
Frequency Identification is a technology, which includes
wireless data capture and transaction processing. Proximity
(short range) and Vicinity (long range) are two major
application areas where RFID technology is used. Track and trace
applications are long range or vicinity applications. This
technology provides additional functionality and benefits for
product authentication. Access control applications are Short
range or proximity type of applications. AgileSense Technologies
is focused on delivering innovative, high value RFID solutions
assisting companys track assets, people and documents.
AgileSense provides robust and complete RFID solutions built on
top of its extensible middleware/framework for Government,
Healthcare, Manufacturing and Aerospace industries.
Asset
Tracking:
Static or
in-motion assets tracking or locating, like a healthcare
facility, wheelchairs or IV pumps in, laptops in a corporation
and servers in a data center, was not so easy task.
User can
instantly determine the general location of tagged assets
anywhere within the facility with the help of active RFID
technology. Control point detection zones at strategic locations
throughout the facility allow the user to define logical zones
and monitor high traffic areas. Tagged assets moving through
these control points provide instant location data.
Asset
tracking applications will see an almost vertical growth curve
in the coming years and the growth rate in this area will be
much higher than the growth rate of general RFID market.

People
Tracking:
People
tracking system are used just as asset tracking system.
Hospitals and jails are most general tracking required places.
Hospital uses
RFID tags for tracking their special patients. In emergency
patient and other essential equipment can easily track. It will
be mainly very useful in mental care hospitals where doctors can
track each and every activity of the patient. Hospitals also use
these RFID tags for locating and tracking all the activities of
the newly born babies.
The best use
of the people tracking system will be in jails. It becomes an
easy tracking system to track their inmates. Many jails of
different US states like Michigan, California, and Arizona are
already using RFID-tracking systems to keep a close eye on jail
inmates.
Document
tracking:
This is most
common problem. Availability of large amount of data and
documents brings lots of problem in document management system.
An RFID document-tracking system saves time and money by
substantially reducing:
-
Time spent
searching for lost document
-
The
financial and legal impact associated with losing documents.
Government
Library:
Many
government libraries use barcode and electromagnetic strips to
track various assets. RFID technology uses for reading these
barcodes unlike the self-barcode reader RFID powered barcode
reader can read multiple items simultaneously. This reduces
queues and increases the number of customers using self-check,
which in turn will reduce the staff necessary at the circulation
desks.
Healthcare:
Patient safety
is a big challenge of healthcare vertical. Reducing medication
errors, meeting new standards, staff shortages, and reducing
costs are the plus points of use of RFID solutions. RFID
wristbands containing patient records and medication history
address several of these concerns.
It is estimated
that RFID activity has impacted on around
250,000 manufacturers, suppliers and
distributors globally, RFID will is now becoming
a must have for organisations wishing to
increase efficiency and profits, these benefits
are mainly realised in the following areas;
-
Improvement in supply chain efficiency
- Providing
visibility for goods in storage and transit.
- Accurate
reporting which leads to reduced stock
outages and reduced inventory levels
- Reducing
time to invoice for deliveries and improved
cash flow
-
Implementing ?Just in time? delivery systems
- Reduced
inventory loss
- Reduced
supply chain shrinkage
- Automated
proof of delivery
- Reduced
labour costs
- Reduced
spoilage
-
Integration with ERP and backend systems
RFID is a
technology that has a huge potential impact on
business processes and systems, it is often
considered as a logical development from the
barcode as a tool for gaining increased
productivity through automation. When used in
conjunction with complementary technologies such
as GPS, GPRS and 802.11* solutions the potential
uses and power for additional automation and
financial savings increases still further. We
will help you decide if RFID is a technology you
should be implementing.

transmitter iriver fm transmitter tracking transmitter
telemetry transmitter futaba transmitter atv transmitter
humidity transmitter uhf tv transmitter dissolved oxygen
transmitter monster fm transmitter transmitter 20w schematic
irock fm transmitter tunecast ii mobile fm transmitter digital
fm transmitter wireless speaker transmitter best ipod fm
transmitter av transmitter honeywell transwireless, zigbee
design contest, product with zigbee zigbee chipsets, zigbee
protocol, zigbee specification, zigbee standard, zigbee hype,
value of the zigbee market zigbee competition, zigbee module uk,
zwave zigbee Transmitter Zigbee Receiver Zigbee Transceiver
Zigbee Remote Zigbee Modules Zigbee Stacks Zigbee 2.4 Ghz, 13.56
Mhz, 125 Khz, Zigbee 900 Mhz, Zigbee 2.45 Ghz, Zigbee dbi, dbm,
Zigbee eirp, Zigbee output input power, Zigbee bandwidth, FSK,
ASK, PSK, QPSK, Zigbee CSMA, OOK, Zigbee DSSS, Zigbee software,
Zigbee hardware, Zigbee products, Zigbee solutions, Zigbee
services, Zigbee systems, Zigbee projects, Zigbee design, Zigbee
engineering, Zigbee development, Zigbee manufacturing, Zigbee
consultancy, Zigbee company, Zigbee networks, Zigbee links,
Zigbee infrastructure, Zigbee data, Zigbee events, Zigbee specs,
Zigbee news, Zigbee tools, Zigbee kits Zigbee resources, Zigbee
markets, Zigbee research, Zigbee books, Zigbee papers, Zigbee
patents, Zigbee technology, Zigbee testing, Zigbee consultants,
Zigbee events, Zigbee instance, Zigbee management, Zigbee
planning, Zigbee problems, Zigbee rejection, Zigbee Chipcon,
Zigbee Freescale Semiconductors, Microchip Zigbee, CompXS
Zigbee, ubec zigbee chip, zigbee ic, zigbee sensors, zigbee home
automation, zigbee building automation, zigbee switch, zigbee
lighting control, zigbee control, zigbee industrial automation,
zigbee india wireless, wireless world, at t wireless india,
cingular wireless, wireless, wireless phone, wireless plan,
wireless network, wireless service, sprint wireless, wireless
internet, prepaid wireless, wireless speaker, wireless router,
liberty wireless, wireless networking, arch wireless
rfid rfid money rfid company rfid dod rfid alien
rfid solution rfid and usps rfid maildefender software rfid and
tag and counterfeiting and copy rfid application build and rfid
and simulator and tag rfid and emulation rfid chips rfid system
label printed rfid rfid journal rfid manufacturer rfid security
system rfid software computer associate rfid software rfid zebra
rfid label rfid matrics rfid insurance property rfid sap rfid
definition rfid ibm rfid computer hardware rfid alien technology
rfid schools rfid samsys rfid gambling casino rfid software
internet security system rfid computer peripheral help with rfid
technology rfid office equipment rfid oracle rfid altiris rfid
sun rfid cable tv rfid transportation rfid medical supply rfid
microsoft software rfid investment services rfid emf software
email rfid thingmagic rfid accenture rfid equipment video rfid
humming bird software rfid livestock rfid equipment audio rfid
red prairie rfid transcore rfid software email protection agency
rfid textile non apparel rfid software internet commerce corp
rfid insurance miscellaneous rfid security services rfid tire
rfid printing industry rfid traxus rfid electronic instrument
rfid t3ci rfid abc software e learning rfid miscellaneous
capital goods rfid construction supply rfid jewelry rfid aquitec
rfid connecterra rfid genuone rfid manhattan rfid shipcom rfid
symantec software rfid manhattan associate rfid bea rfid i2 rfid
provia rfid restaurant rfid airline rfid yantra rfid insurance
accident rfid adobe software rfid beverage non alcoholic rfid
retail apparel rfid cambar rfid oat system rfid singlefin
software rfid sbk lab rfid printing services rfid semiconductor
rfid industry apparel rfid p g rfid globeranger rfid high jump
rfid office supply
About RFID RF Basic Zigbee Module Zigbee Stack Zigbee Modules
Zigbee Products Zigbee Development Kit Zigbee Software Zigbee
Solutions Zigbee modules Zigbee stacks products solutions zigbee
wireless IEEE 802.15.4 rf transceiver transmitter zigbee
products zigbee evaluation kit zigbee alliance zigbee wireless
zigbee design contest Zigbee product with zigbee zigbee chipsets
zigbee protocol zigbee specification zigbee standard zigbee
zigbee hype value of the zigbee market zigbee competition zigbee
module uk zwave zigbee zigbee module zigbee zigbee evaluation
kit zigbee alliance zigbee.
More information about RFID
http://www.rfid-product.com
Zigbee Wireless RFID RF GSM GPS GPRS CDMA
Transmitter Receiver Transceiver Remote Modules Stacks 2.4 Ghz,
13.56 Mhz, 125 Khz, 900 Mhz, 2.45 Ghz, dbi, dbm, eirp, output
input power, bandwidth, FSK, ASK, PSK, QPSK, CSMA, OOK, DSSS,
software, hardware, products, solutions, services, systems,
projects, design, engineering, development, manufacturing,
consultancy, company, networks, links, infrastructure, data,
events, specs, news, tools, kits resources, markets, research,
books, papers, patents, technology, testing, consultants,
events, instance, management, planning, problems, rejection
3G,802.11,802.11a,802.11b,802.11g,802.15,802.16,802,11,15,16,
area, Bluetooth, BREW, CDMA, cellular, EDGE, EMS, GPRS, GPS,
GSM, HiperLAN, HomeRF, IEEE, imode, i-mode, instant, IrDA,
Infrared, Java, J2ME, LBS, Location, OFDM, message, messaging,
mobile, MMS, Multimedia, PAN, personal area networks, PAN,
personal, Positioning,Radio, SMS, Spectrum, SyncML, system,
TDMA, UMTS, UWB, VoiceXML, WAP, WLAN, wireless, Wireless
Internet, WLAN, WPAN, WMAN, XHTML, ZigBee Wireless GSM GPS GPRS
CDMA India, Wireless india, GSM india, GPRS india, CDMA india,
GPS india, Wireless products india, GSM modem india, gsm
controller, gsm m2m, gprs modem , gsm gprs modem, gsm module,
GPS module india, gps modem, gps mouse, gps vehicle tracking
system, remote vehicle tracking CDMA modem, CDMA module, CDMA
controller, CDMA data transfer system wireless networking,
wireless lan, wireless communication, wireless software hardware
system, wireless services solutions products, wireless cheap
free frequencies, MHz Khz GHz, ISM bands frequencies, gps
vehicle tracking, vehicle tracking system, vehicle tracking
device, gps vehicle tracking system, real time vehicle tracking,
vehicle fleet tracking, vehicle tracking uk, wireless vehicle
tracking, real time vehicle tracking system, verizon wireless,
att wireless, at t wireless, cingular wireless, wireless,
wireless phone, wireless plan, wireless network, wireless
service, sprint wireless, wireless internet, prepaid wireless,
wireless speaker, wireless router, liberty wireless, wireless
networking, |
.: Related Products :. 
NFC Contactless Magnetic Mobile card reader

UHF RFID Reader writer

UHF RFID
Reader Antenna




RFID Applications areas

Wireless Products

PCIe Card 3G GSM GPRS Modem

GSM/GPRS module 
4 LTE Module Modem 

 

     

: Useful Links ::
Biometrics
Access Control
Fingerprint Scanners USB
Fingerprint technologies
Biometric Security
Embedded Resource
News
Biometrics Fingerprints Software
eOffice Resources
RFID Modem/Module
Biometrics Access control
OEM Fingerprint
Gold Campaign
Sensors
Software Development Kit
GSM GPRS Products
Axis Network PoE camera
Biometrics services
Wireless Data Terminal
Biometric solutions
Biometrics Time Attendance
Rapidindex Electronics
Fingerprints Standalone Modules
Property Management
Advanced Technologies RFID
Info
Axis Systems
Biometric Product
GSM GPRS Modem
Fingerprints Time Attendance
Electronics Healthcare
Wireless Security
Fingerprints Readers
Electronics
Time Attendance
Biometrics Tech
Fingerprint ID Products
Ayurvedic
Fingerprints Access Control
Time Recorders
Embedded Solution
Biometrics Resources
Mini ITX BOX
Electronics Connectors
|